Fishing is a huge business that brings big economic benefits, while also having an important role to play in providing jobs and food security. The global seafood market is estimated to reach about $138,7 billion by 2027. Despite its international importance, the industry remains a mystery to a large extent.
Limited information and data on vessels’ locations, places where they operate, their owners, the amounts of their catches, and how these stocks are transported leads to illegal activities such as piracy, smuggling, or illegal fishing.

The problem of illegal fishing and its impact on the global seafood market.
The global seafood market depends on a global fleet of fishing vessels. From trawlers to seiners and small boats, fishing vessels come in many sizes, designs, and destinations. This diversity and location make the industry extremely complicated. No one is able to fully estimate the exact number of vessels. And especially, their activities and challenges related to illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing (IUU fishing).
Global estimates suggest a minimum of 20% of seafood worldwide is caught illegally, representing economic losses between $10 to $23 billion and 11 to 25 million metric tons of fish. However, as this is a dark market, and many illegal activities take place at night or under the cover of difficult weather conditions, estimates are understated.

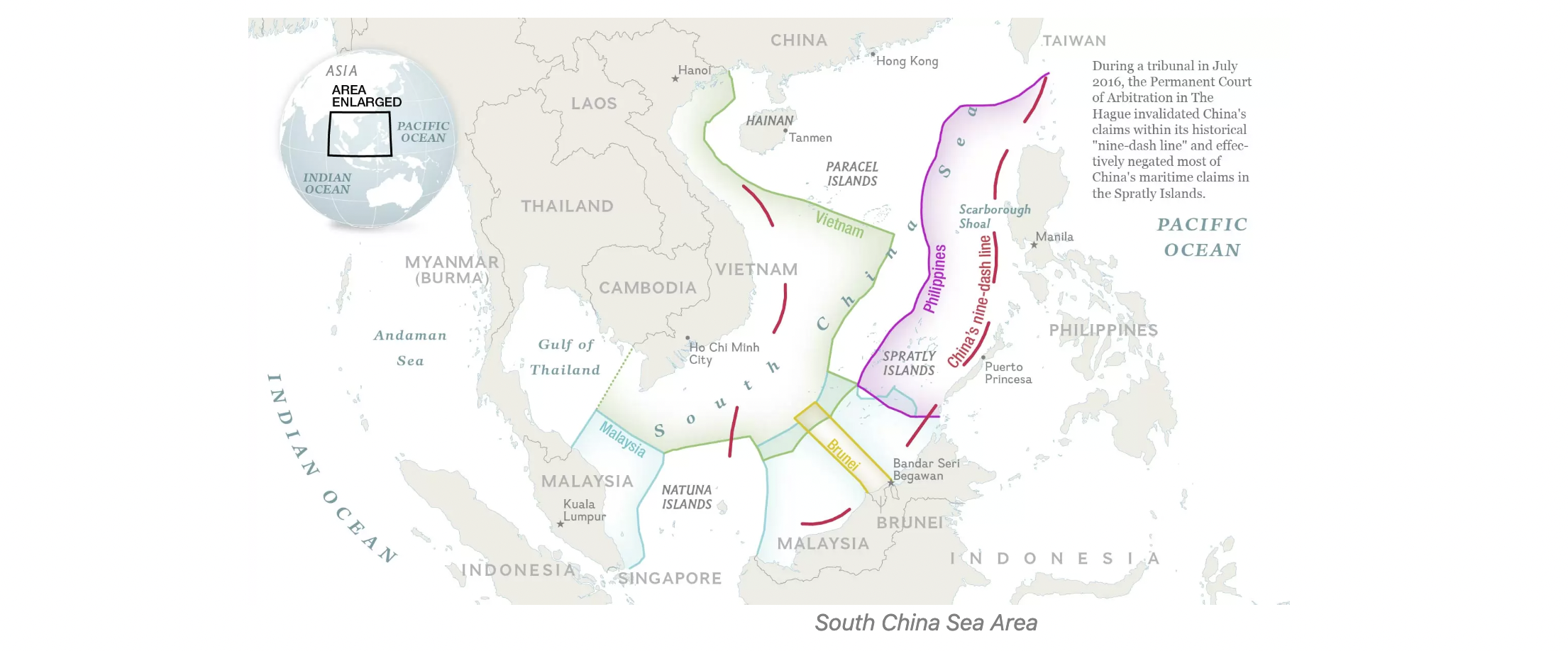
SOUTH CHINA SEA (SCS) and fishing vessels
More than 50% of the fishing vessels in the world are estimated to operate in the South China Sea. This is an area of around 3.8 million square kilometres and is bordered by 12 countries/territories. These places are home to two billion people and represent some of the fastest developing economies in the world. It is one of the top 5 most productive fishing zones in the world in terms of total annual marine production. Moreover, it is one of the zones the most affected by illegal fishing. The South China Sea is currently almost 90% overfished and a very high percentage of fish stocks are used.
It is practically impossible to track all fishing activities in the SCS territories. It is because due to territorial disputes, and difficulties in identifying boats. Maritime activity is usually followed on the basis of Automatic Identification System (AIS), Vessel Monitoring System (VMS), or Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) technologies. This data shows a significant amount of catches in the areas. However, they are not accurate enough to fight illegal activities.
What are the limitations?
The mentioned data is good and relatively inexpensive, the possibility for AIS/VMS sensor interfere is quite common. Many fishing vessels don’t have these systems because they are small and they are under no obligation to use them. Conversely, they may be going dark to intentionally turn off the signal and hide their IUU fishing activities. Many dark vessels are reporting false identification or a series of them in order to distort maritime situational awareness.
Data from meteorological satellite sensors (VIIRS) are generally open access, are available in near real-time, and have long-term archives, but a major disadvantage is their spatial resolution at the level 750×750 m, which is too inaccurate when it comes to vessel detection.
Discover fishing vessels going dark
Thanks to international cooperation and new technology, we can make progress in tracking IUU fishing. Coastal states and the industry are working to improve the transparency and accountability of illegal maritime phenomena. Control systems such as AIS, VMS, or satellite optical images can be significantly supported by satellite radar-based imagery. They are accompanied by AI-based vessel detection and classification algorithms. All of that fills the gaps in understanding the problem and increases transparency in the fisheries sector.
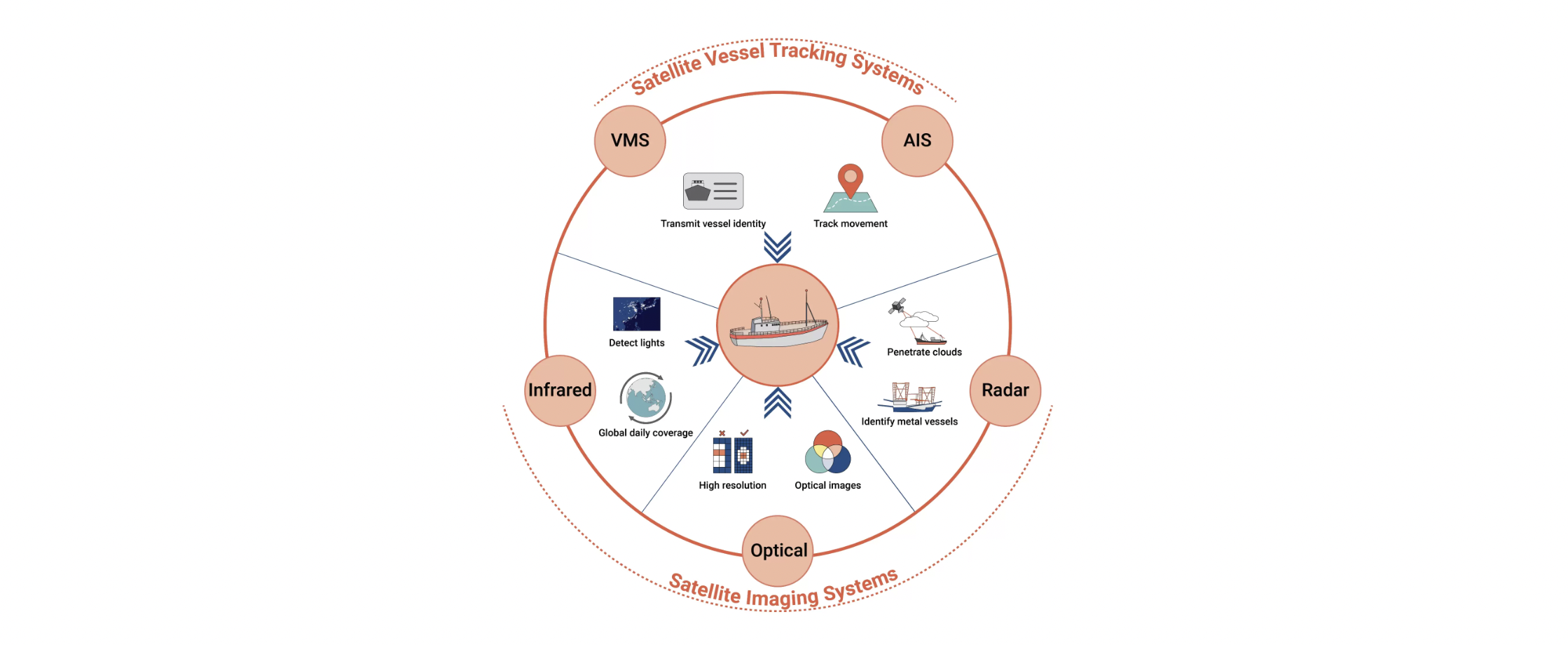
By using SAR imagery you can get a more detailed analysis of fishing activity and improve the traceability of vessels. Everything regardless of weather conditions and of time of day. The effectiveness of actions to combat illegal fishing depends on many factors. The quality of the data, the ease of obtaining it, and our ability to interpret it, for instance. SAR data with sub-meter resolution is already available on the market. New opportunities allow the development of AI-based solutions. Finally, a new era of SAR will come, where commercial access to data will be possible and simple.
So, let’s make SAR easy and improve the monitoring of seas and oceans. It will be crucial if we hope to save our fisheries and our oceans. If you would like to know more about SATIM, our technology, or products please contact us hello@satim.co










